A modified minimal gated unit (MGU) structure
10 Mar, 2021Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are versatile structures used in a variety of sequence data-related applications. The two most popular proposals are long short- term memory (LSTM) and gated recurrent unit (GRU) networks. Towards the goal of building a simpler and more efficient network, minimal gated unit (MGU) has appeared and shown quite promising results. We present a simple and improved MGU model, MGU_1 in this blog.
If you are not familliar with RNNs, you can check this link.
The code of this blog is on Github repo.
MGU
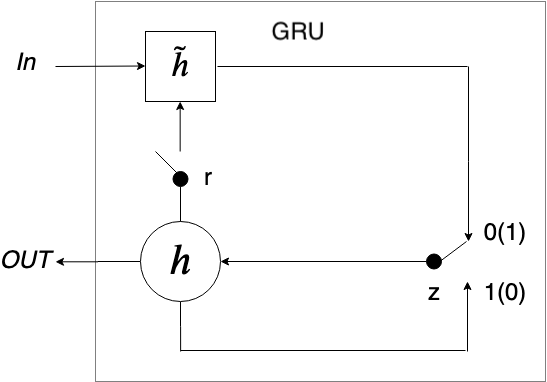
MGU is introduced to further lower complexity and maintain comparable accuracy when comparing to GRU. There are two gates in the GRU to control the data flow. As illustrated in the figure below, the reset gate and the update gate both control the portion of input and the previous hidden state in the current hidden state, there must be a correlation and redundancy between these two gates. Micro et al. [2] have proved the correlation by cross-correlation. Using the same value for the reset gate and update gate, therefore, is a natural operation. The MGU has only one gate - the forget gate () - to represent the two gates above as below:
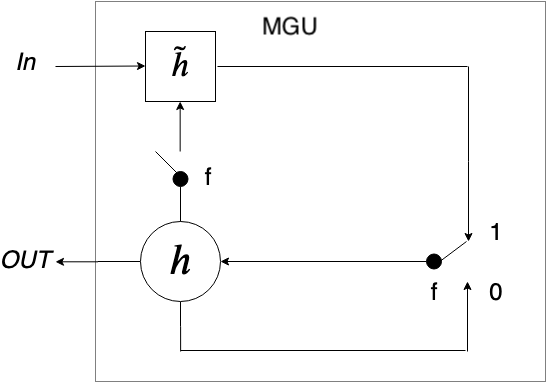
MGU optimization
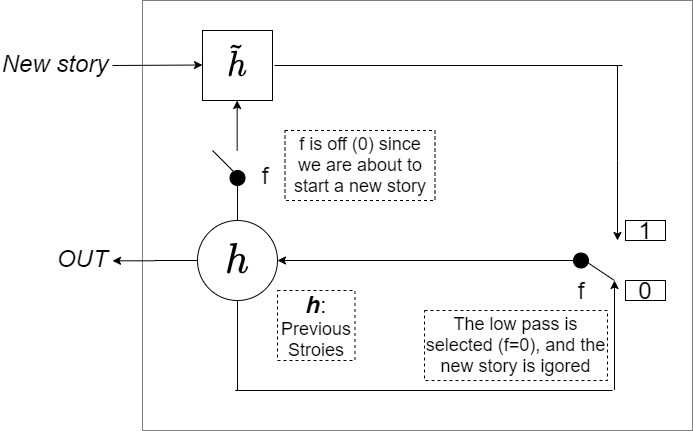
In MGU model, when the forget gate is 0, the previous hidden state will be cut off from flowing to the candidate hidden state (left switch is off). As a result, for the example below, the candidate hidden state only contains the input of the new story. We want to forget about the previous stories since it is a fresh start. However, for the switch on the right, when the forget gate is 0, the previous hidden state ( ) - which contains previous stories - will be put through, and the candidate hidden state () - which contains the new story - will be drop off. This indicates that the logic of the two gates conflict with each other.
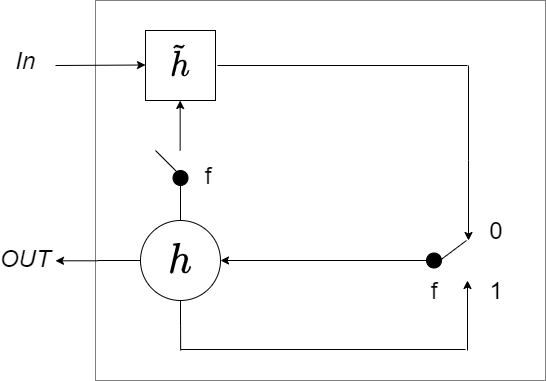
The easiest way to solve this is to switch the pole of the right switch as below:
Experiment
The PTB data set is widely used in natural language processing (NLP) research. We use this data set for the word prediction task and consider the model in [2] as a reference. The size of the vocabulary is 10,000. It has 929k words for training and 73k words for validation. The model contains 2 layers of RNN and each has 200 hidden units. The time steps and batch size are set to 30 and 20 separately. A dropout layer is used and set the drop out rate to 0.2. Then a fully connected layer predicts one of the 10,000 words at the output.
The result of GRU, MGU and MGU_1 (optimized version) is shown in figure below. The performance of MGU_1 is on par with GRU and better than MGU. The MGU and MGU 1 layers both have 160,400 parameters in RNN layer, while the GRU layer has 241,200 parameters.
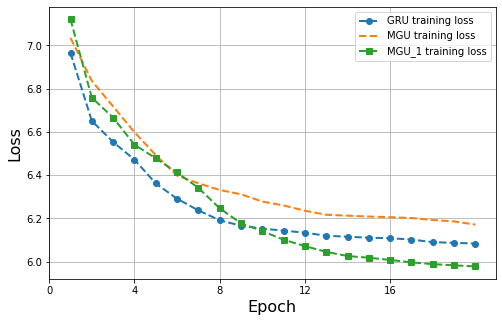
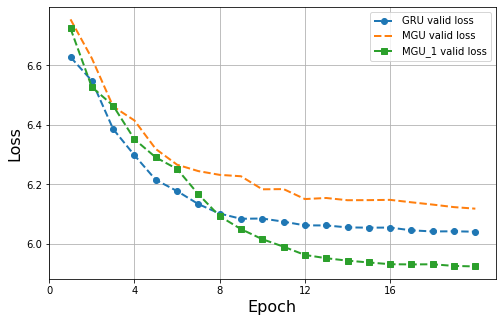
Conclusion
Logic analysis can be one important process when we create a new RNN structure. Any logic conflict may lower the performance of the network.
By the way, in [2] they proposed a struture that removed the reset gate in GRU and only keep the update gate. I compare the performance of this proposal with the MGU_1. The former one is not as stable as the latter one (sometimes not converge). But when using Relu as the activation function, their performance is on par and they are both stable.